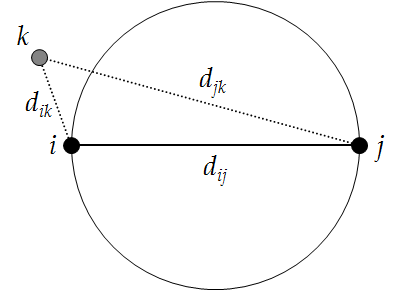
In a Gabriel Graph, a connection scheme proposed by Gabriel and Sokal (1969), two points are connected when the circle (or sphere in three dimensions) associated with the diameter that has the two points as endpoints does not have another point within its circumference (volume).

Diagram explaining the Gabriel Graph.
Mathematically, two points i and j are connected if the square of the
distance between them,![]() , is less than the sum of the
squared distance between each of these points and any other point k.
, is less than the sum of the
squared distance between each of these points and any other point k.
Connect i and
j if ![]() for
all k
for
all k
The relative neighborhood network is a subset of the Gabriel graph. See Gabriel and Sokal (1969) and Matula and Sokal (1980) for more information on Gabriel Networks and their properties.
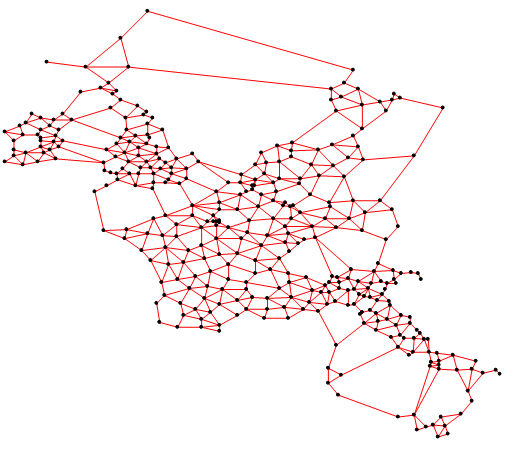
Example of a Gabriel graph.